
What is E-Waste? The Shocking Truth You Need to Know!
Introduction
Electronic Waste or E-waste has become one of the most significant challenges facing the world today. With the rapid advancement of technology, we are generating more electronic devices than ever before, and their disposal has become an issue that cannot be ignored. E-waste refers to the discarded electronic items such as computers, smartphones, televisions, and other electronic devices that are nearing the end of their useful lives. These electronic devices are often hazardous and contain toxic components that can cause significant harm to our environment and human health. This article will provide you with a comprehensive guide to e-waste, the impact it has on our world, and practical solutions to reduce its effects.
What is E-Waste?
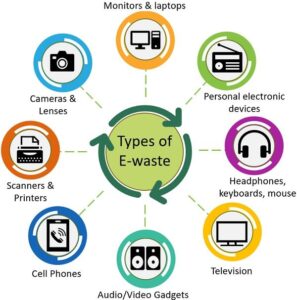
Electronic waste or e-waste refers to electronic devices that are near or at the end of their useful life span and are discarded. These devices often contain hazardous materials such as lead, cadmium, mercury, and other toxic chemicals that are harmful to our environment and health if not disposed of correctly. E-waste includes several types of devices, such as:
Types of E-Waste:
Definition and Types of E-waste
- Personal computers, laptops, and printers
- Mobile phones, smartphones, and tablets
- Televisions, DVD players, and home entertainment systems
- Power tools, and other electrical devices
- Batteries, including lithium-ion and nickel-cadmium batteries
- Electronic components and wires
What Is E-Waste?
Examples of Common E-Waste Items
Some common e-waste items include:
- Personal computers and laptops
- Printers and copiers
- Televisions and home entertainment systems
- Mobile phones and smartphones
- Batteries and chargers
Reasons Why E-waste is Generated
The rapid advancement of technology has led to the generation of more electronic devices, and with each new product comes a shorter lifespan of older ones. Here are some reasons why e-waste is prevalent:
Planned Obsolescence
Electronic devices are designed with a limited lifespan, compelling consumers to purchase newer products frequently. Manufacturers intentionally create products that will become obsolete so that consumers will buy new ones as often as possible.
Advancements in Technology
As technology gets advanced, newer products offer better features with more efficiency, and old devices become outdated and are discarded.
Discarding of Old Items
Old electronics that are still usable are often thrown away because users don’t know what to do with them.
The Impact of E-waste
The improper disposal of electronic waste can have a significant impact on our health, environment, and economy. Here are some of the impacts of e-waste:
Environmental Impact
Electronic waste poses a severe threat to our environment as electronic devices often contain toxic chemicals. When they are sent to landfills, these toxins contaminate soil and groundwater, making them unsafe for human and animal use.
Toxic Chemicals
Discarded electronics contain toxic materials such as lead, cadmium, mercury, and other hazardous substances. These toxic materials have adverse effects on both human and animal health.
Pollution of Air and Water
Improper disposal of e-waste produces harmful gases that pollute the air. These gases contribute to climate change, global warming, and other environmental problems. Electronic waste can also contaminate water resources by leaking hazardous chemicals and polluting water supplies.
Health Impact
The toxic materials found in electronic waste pose a severe threat to human health. These toxins cause severe health problems such as cancer, respiratory problems, and organ damage.
Risks to Human Health
Improper disposal of e-waste can cause harm to people who are in direct contact with it. For example, workers at recycling plants handling e-waste are at risk of exposure to toxic chemicals.
Effects on Wildlife
E-waste poses severe threats to wildlife and their habitats. Wildlife can mistake electronic waste for food and consume toxic substances, resulting in health problems and even death.
Economic Impact
Electronic waste disposal is a significant economic burden. The cost of disposing of electronic waste can be high, and there is also a loss of valuable resources.
The Cost of Disposal
Disposing of electronic waste is expensive. Recycling centers charge fees for accepting electronic waste, and the cost of shipping electronic waste to recycling facilities can be high.
Loss of Valuable Resources
Electronic devices contain valuable materials such as gold, silver, and copper. These materials can be recycled to make new products, preserving important resources.
Recycling Process at Gravity E-Waste Management
How to Reduce E-waste
To combat the problem of e-waste, it is essential to take a proactive approach in reducing e-waste. Here are some strategies:
Extended Producer Responsibility
Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) is a legal framework that holds manufacturers responsible for the entire lifecycle of their products, including disposal.
Consumer Responsibility
Consumer behavior plays a crucial role in reducing e-waste. Consumers can take steps such as repairing broken devices and donating used electronics to reduce electronic waste.
Recycling E-waste
Recycling e-waste is one of the most effective ways of reducing electronic waste. Recycling reduces the negative impact of e-waste by recovering valuable materials and reducing the amount of hazardous waste sent to landfills.
Donation of Working Electronics
Donating working electronics to non-profit organizations such as schools or charities can help prolong the life of electronic devices and reduce e-waste.
Refurbishment of Old Electronics
Refurbishing old electronics is an excellent way of reusing them. Old electronic devices can be refurbished by upgrading them, extending their useful life.
Purchasing New Electronics Responsibly
When purchasing new electronics, consumers should opt for products manufactured by companies that have sustainable recycling and disposal processes
Where Does E-waste Go?
E-waste can end up in two places: formal recycling centers or informal, unregulated centers in developing countries.
Informal E-waste Recycling in Developing Countries
Informal e-waste recycling centers often operate outside of the legal framework and lack adequate safety standards. These workers are often subject to hazardous working conditions and exposure to toxic materials.
Dangers for Workers
Workers at informal e-waste recycling centers are at risk of exposure to hazardous materials such as lead, cadmium, and other toxic chemicals. Exposure to these toxic materials can cause severe health problems, including cancer and organ damage.
Formal E-waste Recycling
Formal e-waste recycling centers follow regulations and safety standards to ensure proper disposal and handling of electronic waste. Formal recycling centers are essential to reduce e-waste and protect workers and the environment.
Potential Benefits
The proper disposal of e-waste in formal recycling centers can recover valuable materials such as gold, copper, and silver, reducing the demand for virgin materials.
Challenges and Limitations
The proper disposal of e-waste comes with several challenges such as high costs of recycling. Even with established formal recycling centers, most e-waste still ends up in developing countries without proper regulation and safety standards.
E-waste Laws and Regulations
Governments worldwide have implemented several regulations and laws to address e-waste management. Here are some of them:
National Legislation on E-waste
Countries worldwide have enacted legislation to address electronic waste. These laws outline the proper handling, storage, transport, and disposal of electronic devices.
International Treaties and Conventions
International treaties and conventions address electronic waste on a global scale. These conventions include regulations governing the shipment and disposal of electronic waste.
Compliance and Enforcement Issues
Lack of funding, awareness, and corruption in some countries remain to be significant barriers to the efficient enforcement of these regulations.
Current Trends and Solutions
Here are some current trends and solutions in the e-waste industry
E-waste Management Strategies
Several waste management strategies involve the proper handling, storage, transport, and disposal of electronic waste.
E-waste Innovations
Companies worldwide are developing innovative ways to reduce e-waste, such as using organic or biodegradable materials to manufacture electronic devices.
E-waste Awareness Campaigns
Awareness campaigns educate the public on the importance of recycling electronic waste and reducing electronic waste’s negative impact on the environment.
E-waste and the Future
The future of e-waste lies in technological advancements and consumers’ behavior. Consumers need to be more responsible for the disposal of electronic waste, and companies need to adopt more sustainable methods of manufacturing.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions about electronic waste:
What is the main reason for e-waste?
The rapid advancement of technology and consumer demand result in frequent upgrades of electronic devices.
What happens when e-waste is not recycled?
Electronic waste that is not recycled often ends up in landfills or informal recycling centers, where they are not disposed of properly, resulting in environmental harm and health risks.
Can e-waste harm your health?
E-waste contains toxic materials that can have adverse effects on human health, causing severe health problems such as cancer, respiratory problems, and organ damage.
How can I recycle my e-waste?
Electronic waste can be recycled by taking it to the nearest recycling center, donating it to non-profit organizations, or refurbishing old electronics to extend their life
Conclusion
Electronic waste is a significant issue that deserves our attention. Disposing of electronic devices can cause severe harm to our environment and health. Governments, industry players, and consumers must work together to reduce the negative impact of electronic waste by adopting sustainable disposal methods, recycling, and donor programs. The future of our planet and human health lies in our hands. Let’s do our part.

